Last Updated on March 14, 2025
What is ERP? And how does it impact the running costs of your central heating and hot water?
Energy-related products (ERPs) account for approximately 55% of the UK’s total
non-transport in-use energy consumption.
ERP policies are one of the most cost-effective ways to reduce carbon emissions and energy costs. They also help drive innovation and bring down product purchase prices for better-performing goods.
You may have noticed various energy-efficient ratings listed on electric appliances when browsing online or within retail settings.
The ERP provides crucial information when buying an appliance and gives useful insight into its quality.
As the UK becomes more aware of the impact of global warming and carbon emissions, the ERP can markedly help households make wiser choices.
ERP can make choosing the most energy-efficient electrical devices and heating systems easier, consequently helping you save money and reduce environmental impact.
But what is ERP?
This guide explores everything you need to know about the ERP. It explains what ERP is, how it works, ERP labels, and how ERP can help you choose an efficient boiler.
Key Takeaways:
- The ERP is a directive that aims to improve the efficiency and performance of energy-related appliances like boilers.
- You can use the ERP rating to determine the level of energy efficiency of a boiler.
- The ERP features a clear, easy-to-understand color-coded letter scale from G (the lowest rating) to A (the highest rating).
- UK regulations require boilers to have an ERP rating of at least 92%.
How old is your boiler? Should you consider repairing the boiler or looking at the latest boiler prices? It’s no secret that boiler efficiency deteriorates over time.
What is ERP?
ERP stands for Energy Related Products Directive. The EU introduced the ERP Directive legislation to improve the efficiency and performance of heating and hot water products.
The ERP came into effect in 2010, replacing the old Energy-using Product (EuP) Directive, which featured a limited scope.
The EuP Directive only included products directly using energy, such as computers or air conditioners. The ERP directive covers products that use energy directly and those that impact energy consumption.
The directive sets a mandatory framework that the manufacturing industry must follow. Specifically, it must focus on sustainability and reducing energy use throughout all stages of product design, development, production, transportation, and packaging.
The ERP also aims to make it easier for end users to determine the level of energy efficiency inherent in their appliances.
Want to learn how to use your boiler better? Read our complete guide on boiler flow temperature, how to optimise your boiler settings, and find out how much gas a boiler uses here.
Why Does the ERP Matter to You and Your Home?
The ERP Directive requires manufacturers to consider all environmental considerations when developing and manufacturing products. This includes the use of water, materials used, emissions created, waste production, and end-of-life management such as recycling.
The ERP generally defines the minimum performance levels products must meet to ensure end-users get more resource and energy-efficient products.
Since your appliances and energy-efficient products directly impact your gas and electricity bills, it only makes sense to purchase appliances designed to increase energy efficiency.
The legislation covers all products made and imported throughout the EU, and the manufacturers and importers are responsible for ensuring that products are compliant.
Following the end of the Brexit transition process, the UK updated its manufacturing legislation, ‘Eco-design of energy-consuming products,’ regarding the environmental impact of products.
Wondering which boiler manufacturers performed best? Check out our best boiler brands guide for the full rundown and if you are trying to determine who the best boiler installation company is, check out our Warmzilla and Boxt reviews.
How Does ERP Work?
The Energy Related Products Directive has two parts: The Eco-design element and the Energy Labelling element as follows:
Eco-design
Eco-design aims to phase out the least efficient energy-related products from the market using minimum energy performance standards.
Requirements under ecodesign also aim to facilitate progress toward a more circular economy by setting requirements for resource efficiency. These include emissions, durability, pollution and waste generation, repairability, and recyclability.
Manufacturers must ensure their products meet various energy-saving criteria during manufacture and use.
Government guidance for manufacturers, authorised representatives, and importers lists various covered products. These include air heating products, solid fuel boilers, water heaters, hot water storage tanks, and solar device and water heater packages.
If energy-consuming products pass specific tests to ensure they comply with specific health, safety, and environmental protection standards, then manufacturers or importers can sell them across the EU.
Manufacturers can only sell products that comply with energy performance guidelines. Overall, any low-rated appliance that doesn’t meet the requirements is prohibited from sale.
For example, ERP eliminates non-condensing boilers up to 400kW, from being placed on the market by boiler importers and manufacturers.
Energy Labelling
Energy labelling aims to encourage the uptake of the most energy-efficient products. It ensures consumers get information on the energy performance of products at the point of sale.
Consumer purchasing decisions are crucial in limiting the environmental impacts of energy-related products.
Overall, providing useful product information allows consumers to make informed purchasing decisions and encourages them to buy more energy-efficient products.
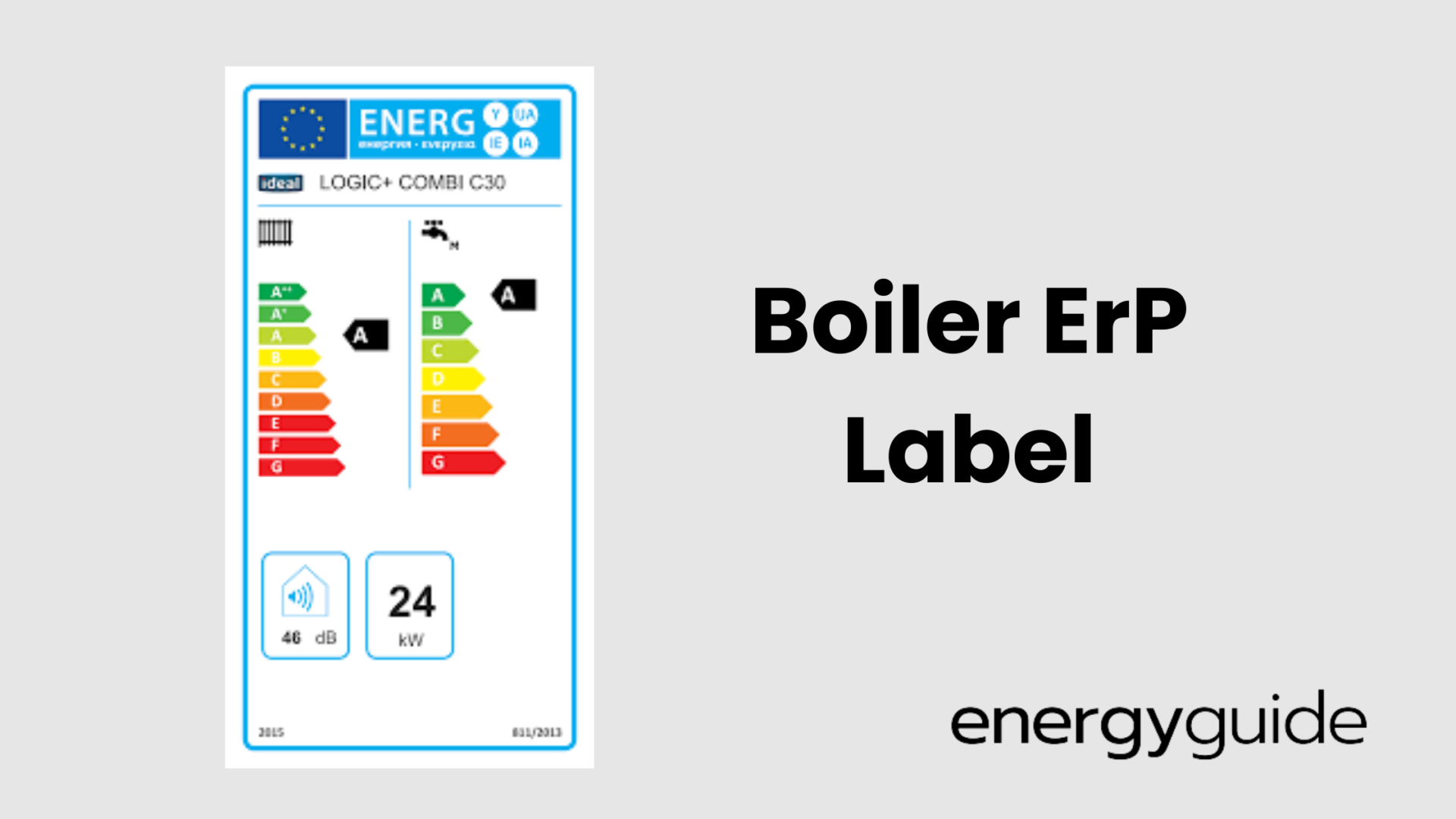
This part of the directive outlines instructions on the labelling of products. Presently, labels must show how energy-efficient a product is using a clear, easy-to-understand color-coded letter scale from G (the lowest rating) to A (the highest rating).
Previously, the scale ran from G to A+++ but was rescaled in 2021. It involved reducing the number of rating classes and removing classes for products below established minimum standards. Moreover, it reclassified the top class of products to A and also kept it empty to allow room for innovation.
What is ERP Legislation Effect on Boilers?
In 2018, the UK government introduced Boiler Plus Standards, setting a minimum ERP rating that all new boilers must meet.
New Installations since April 2018 must meet these standards of having at least 92% ERP efficiency rating as well as time and temperature control.
In addition, combi boilers must add one of the following elements:
- Weather Compensators– An additional device that adjusts the radiator temperature based on the external temperature. Such a device will add around £20-£30 to the installation cost. However, it’s likely to save the household money on energy bills.
- Load Compensators – Load compensation controls use the difference between the internal room temperature and the desired room temperature set on the thermostat to control the boiler’s output to close the gap and reduce the flow temperature needed for the radiators.
- A Flue Gas Heat Recovery (FGHR)– FGHR systems recover heat from waste flue gases to preheat the cold water entering the boiler. They provide efficiency gains by reducing the energy required to warm the water to the required temperature. Installers fit FGHR systems alongside combi boilers as an additional unit attached to or integrated within the boiler.
- Smart Controls – Smart controls allow you to remotely control the heating and hot water system from anywhere via an app on smartphones, tablets, or computers. To this end, they should feature automation or optimisation if they don’t have weather or load compensation.
What is the Latest Position on Boiler Plus Legislation?
The latest government response on improving boiler standards and efficiency features various proposals to emphasize commitments to reduce emissions to net zero, save families money on energy bills, and address climate change. These include:
- Introducing changes through ecodesign and energy labelling regulations to prevent the sale of certain products on the market and improve boiler efficiency. As such, it aims to prevent the sale of heating Control Classes I-III (the worst-performing simple controls) on the market by 2026.
- Mandating that combination boilers and all controls be capable of using open protocols by 2026. As a result, the government will require the use of OpenTherm if a new open protocol isn’t available. OpenTherm is already popular in a significant portion of the market.
- Ensuring boilers that are 45kW and under can modulate their heat output down to 15% of their maximum output without on/off cycling. In addition, they must operate at the same efficiency as when tested at part load.
What is ERP Boiler Efficiency and How Does it Work?
Boiler efficiency refers to how well your boiler converts fuel into heat. Manufacturers generally calculate it as a percentage of how much fuel the boiler converts into usable energy and how much is wasted in the process.
For example, if you have a boiler that is 90% efficient, it will use 90% of the fuel to heat the water and waste 10%. The higher the boiler efficiency, the less fuel it uses, eventually helping you reduce energy bills and lower carbon emissions.
Afterward, the boiler is given an ERP letter rating based on the calculations. Most boilers with an efficiency of 90% and above are usually A-rated. You can check the rating on the boiler’s label.

Occasionally, some manufacturers also use the SEDBUK rating system, which was replaced in 2015 by the ERP rating system. They believe it offers a more accurate reflection of the boiler’s yearly efficiency to help consumers choose the right boiler.
Did you know the efficiency of your boiler can impact the amount of energy it uses and ultimately impact your heating bill costs? Check out our guide to the best condensing boilers to find out more.
Check out our video on how to vet boiler brands/models in the UK:
You may also find our review of the best eco-friendly boilers of interest.
Have you heard about the gas boiler ban and are wondering what the alternatives to gas boilers are? Read our complete guide to replacing your gas boiler with a heat pump.
What Are the Benefits of An Efficient Boiler?
Lower Energy Bills
Modern A-rated boilers are significantly better at using less fuel than old, inefficient boilers. They can use less fuel to heat your home and help you save money on energy bills.
According to the Energy Savings Trust, replacing an old gas boiler with a new A-rated condensing boiler can save you from £215 to £475, depending on your home’s size and thermal performance.
Reduced Carbon Emissions
Efficient boilers convert more fuel to heat your home and are designed to emit fewer greenhouse gases. Upgrading to a high-efficiency boiler can help reduce your carbon footprint and promote a cleaner, more sustainable future.
Increased Property Value
Installing a high-efficiency boiler can make your property more attractive to potential buyers.
A high-efficiency boiler can increase the resale value of your property as more homeowners are looking for greener homes that can provide long-term savings on energy bills.
Lower Maintenance Costs
High-efficiency boilers can lead to lower maintenance costs in the long term. They’re built with durable materials and advanced components, making them less prone to malfunctions and breakdowns.
Most manufacturers also offer extended warranties for high-efficiency models, giving you peace of mind and protection for your investment.
Compatibility with Renewable Energy
Newer, high-efficiency boilers are compatible with renewable technologies like solar thermal panels or biomass boilers. Integrating these renewable sources with your boiler can further increase energy savings and reduce your carbon footprint.
What Are the Boiler Flue Regulations 2018?
In addition to the regulations regarding the boiler itself, the 2018 regulations also state that a boiler flue must be installed within a specific location due to the potential danger of hazardous gases produced by the boiler.
The regulations require the installation of a standard-sized boiler’s flue at least 30cm away from an opening like a window or door.
For larger boilers, the distance should increase to 60cm. However, if these distances cannot be met, the flue should be at least 2.1 metres high.
These changes ensure the boiler’s flue position is installed in the safest position on a property to prevent any escaped gasses from causing harm.
The table below shows some additional flue distance requirements:
| Flue Position | Required Distance |
| Below temperature-sensitive components like plastic gutters and soil pipes | 75mm |
| Below eaves | 200mm |
| Below balconies or Carport roof | 200mm |
| From a vertical drain pipe or soil pipe | 150mm |
| From an internal or External corner | 300mm |
| Above-ground roof or balcony | 300mm |
| From a surface facing the terminal | 600mm |
| From a terminal facing the Terminal | 1200mm |
| From an opening in the carport Into the dwelling | 1200mm |
| Vertically from a terminal On the same wall | 1500mm |
| Horizontally from a terminal On the same wall | 300mm |
Got a common boiler problem? Check out our quick-fix guide on boiler lockout, boiler ignition faults, boiler PCB faults, faulty diverter valves, and boiler timer issues.
Summary on What is ERP
Homeowners are becoming more aware of their environmental impact and how being more energy efficient can help reduce their household’s carbon footprint.
ERP ratings make it easier to make an informed decision when looking for a new boiler. they can help you find a modern, highly efficient boiler that complies with government standards and regulations.
Small changes like choosing highly energy-efficient devices when replacing older models, turning off devices when not in use, and using smart technology can greatly impact your energy bills.
If you’d like to learn more about the ERP framework, the SEDBUK system, or which boiler system and fuel type would be most suitable for your property, please get in touch. Our knowledgeable heating engineers can provide further assistance and ensure your new installation complies with regulations.
Sources and References
- https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/61965c26d3bf7f05522e2d8f/energy-related-products-policy-framework.pdf
- https://www.gov.uk/guidance/placing-energy-related-products-on-the-uk-market
- https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/660c52b9fb0f770011ec66da/improving-boiler-standards-and-efficiency-consultation-government-response.pdf
- https://energysavingtrust.org.uk/advice/boilers/
Further reading: